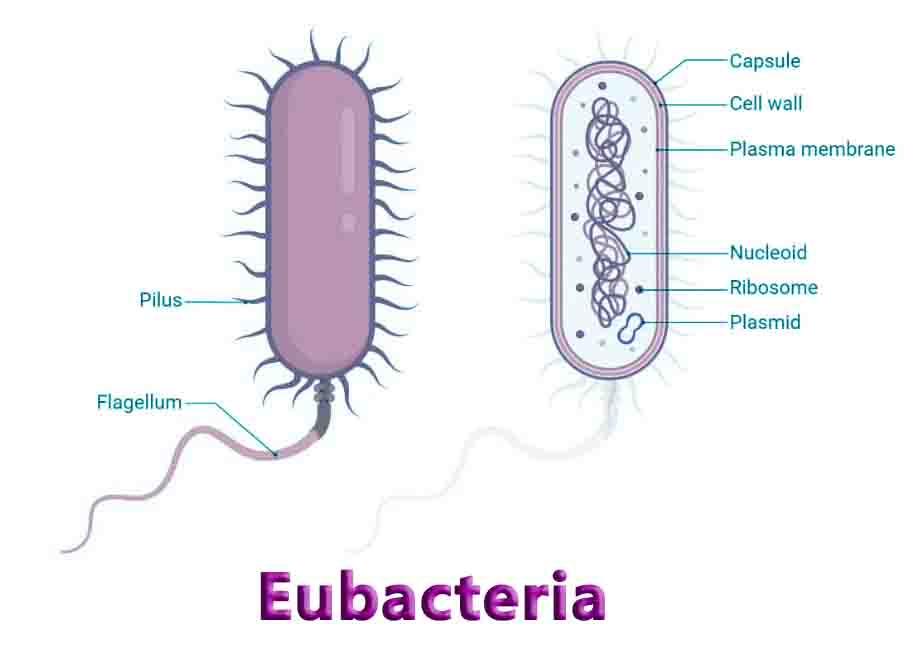
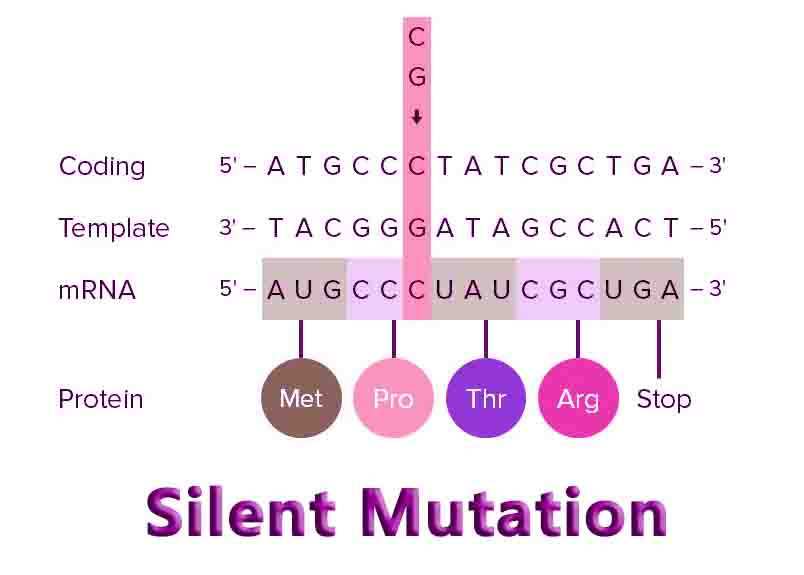
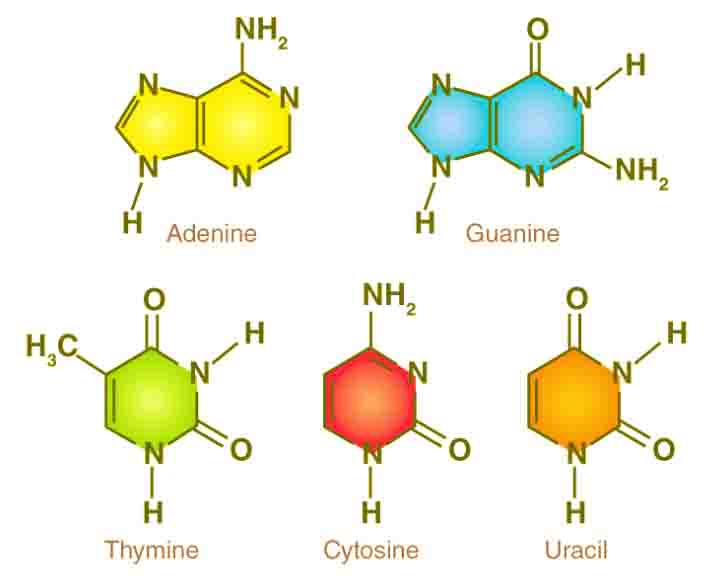
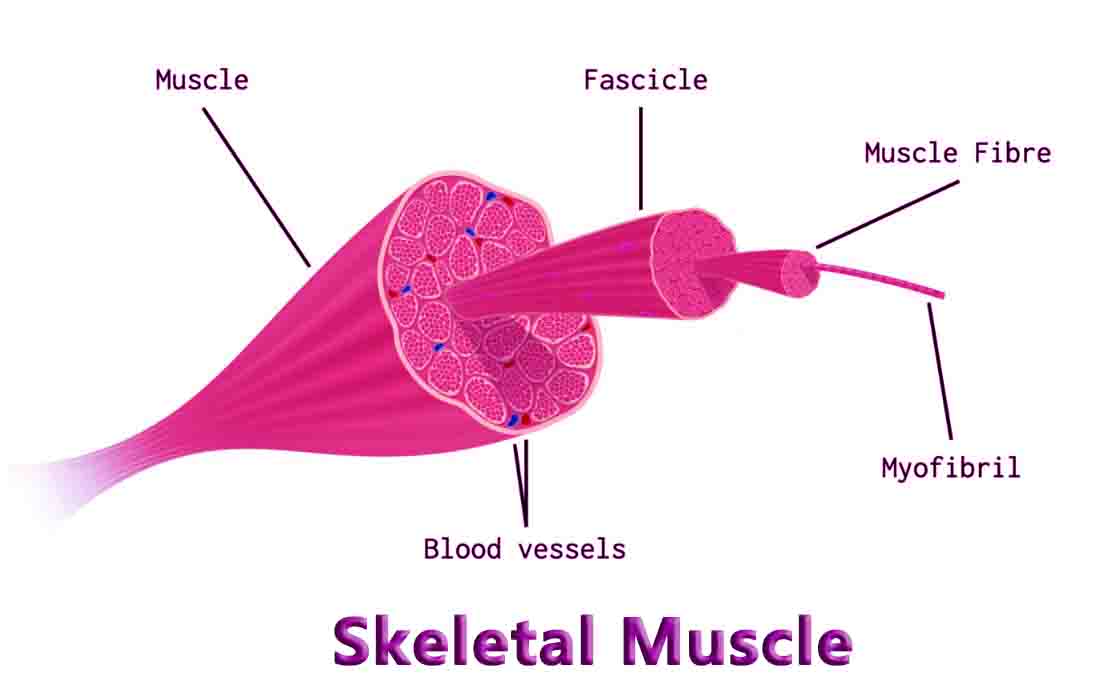
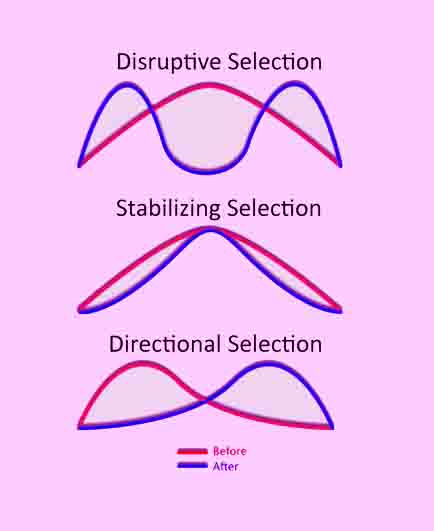
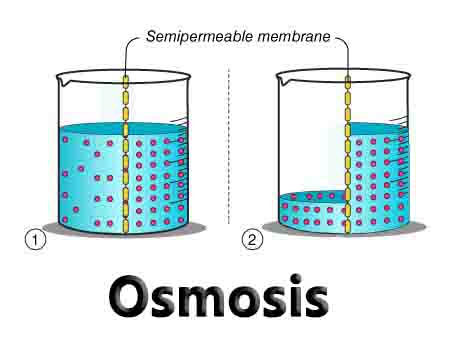
The Benefits of IB Applications and Interpretations
In today’s rapidly evolving world, the importance of practical applications in education cannot be overstated. As industries and job markets shift, the demand for real-world skills has surged. Students are no longer just required to memorize facts and theories; they need to apply their knowledge in practical, meaningful ways. This shift is evident across various … Read more